As our world becomes increasingly dependent on electronic devices, the issue of e-waste management continues to grow. Every year, millions of tons of electronic waste—ranging from smartphones and laptops to large appliances and industrial machinery—are discarded. This has created an environmental challenge that demands urgent attention. However, new technologies like Zero Waste Discharge Technology (ZWDT) are offering a sustainable solution to this problem.
In this blog, we will explore the role of zero waste discharge technology in e-waste management and how it can reshape the future of sustainable recycling practices.
What is Zero Waste Discharge Technology?

Zero Waste Discharge Technology is an advanced recycling process that ensures no harmful waste is released into the environment during the e-waste recycling process. It is designed to recover and reuse as many components of electronic waste as possible while minimizing or eliminating the discharge of hazardous materials.
Traditional recycling methods often involve burning, shredding, or chemically treating e-waste, which can lead to the release of toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium into the air, water, and soil. Zero Waste Discharge Technology, on the other hand, emphasizes clean recycling processes that prevent these harmful materials from polluting the environment.
The core philosophy behind zero waste discharge is simple: everything that can be reused, repurposed, or recycled should be, with the ultimate goal of diverting all waste from landfills and incinerators.
The Growing Need for Sustainable E-Waste Management

The global e-waste problem is reaching critical levels. According to the Global E-Waste Monitor, the world produced 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, and this number is expected to grow to 74 million metric tons by 2030. Unfortunately, only about 17.4% of e-waste is formally collected and recycled, leaving a vast majority of this waste improperly handled.
The improper disposal of e-waste poses serious environmental and public health risks. Toxic materials found in electronic devices can leach into groundwater, contaminate the soil, and release harmful gases into the atmosphere when burned. The impact on climate change, biodiversity, and human health is alarming.
This is where Zero Waste Discharge Technology comes into play. By offering a clean and efficient method for recycling electronic waste, ZWDT provides an effective solution to reduce the environmental footprint of e-waste while recovering valuable resources.
How Zero Waste Discharge Technology Works
The goal of Zero Waste Discharge Technology is to recycle e-waste in a way that leaves no harmful byproducts and ensures that nearly all components of e-waste are either repurposed or safely processed. Here’s how the process works:
Collection and Sorting
E-waste is collected from various sources—individuals, businesses, and government agencies—and transported to a certified recycling facility. Once the e-waste arrives, it is sorted into categories based on material composition and recyclability. This includes separating materials such as metals, plastics, and hazardous substances.
Dismantling and Decontamination
The dismantling process involves carefully breaking down electronic devices into their individual components, such as circuit boards, glass screens, and batteries. Toxic substances like mercury, lead, and cadmium are safely removed and treated using advanced decontamination processes to ensure they don’t pose a risk to human health or the environment.
Material Recovery
Using advanced techniques such as mechanical shredding, hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, the remaining components are processed to extract valuable materials like gold, silver, copper, aluminum, and rare earth metals. These materials can then be reused in the production of new electronics, supporting the creation of a circular economy.
Safe Disposal of Non-Recyclables
Materials that cannot be recycled, such as certain types of plastics or hazardous chemicals, are treated and disposed of using environmentally safe methods. This ensures that no toxic materials are left behind, reducing the need for landfills and preventing environmental contamination.
The Environmental Benefits of Zero Waste Discharge Technology
The environmental benefits of Zero Waste Discharge Technology are vast, making it a key player in the fight against e-waste pollution. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
Reduction of Toxic Waste
One of the biggest challenges of e-waste management is handling the toxic chemicals and heavy metals found in electronics. These substances can cause severe harm to the environment if they leach into soil or water systems. ZWDT ensures that these toxic components are safely removed, treated, and either repurposed or disposed of without contaminating the environment.
Resource Conservation
E-waste contains valuable materials such as gold, silver, platinum, and copper, which can be recovered through zero waste discharge recycling methods. By recovering and reusing these materials, we reduce the need for mining and extraction, which are both energy-intensive and environmentally destructive. This approach conserves natural resources and reduces the overall environmental impact of electronic production.
Energy Efficiency
The production of new electronics from raw materials requires significant amounts of energy. By recycling materials through ZWDT, the energy required to produce new products is greatly reduced. For example, recycling aluminum uses 95% less energy than producing it from raw materials. This translates to lower carbon emissions and a reduced carbon footprint for the entire electronics industry.
Minimizing Landfill Waste
Traditional e-waste disposal methods often involve dumping electronic waste in landfills, where it can take hundreds of years to break down, releasing harmful substances into the surrounding environment. With Zero Waste Discharge Technology, the volume of e-waste that ends up in landfills is dramatically reduced, helping to alleviate the pressure on overburdened landfill sites and preventing further environmental degradation.
Supporting a Circular Economy
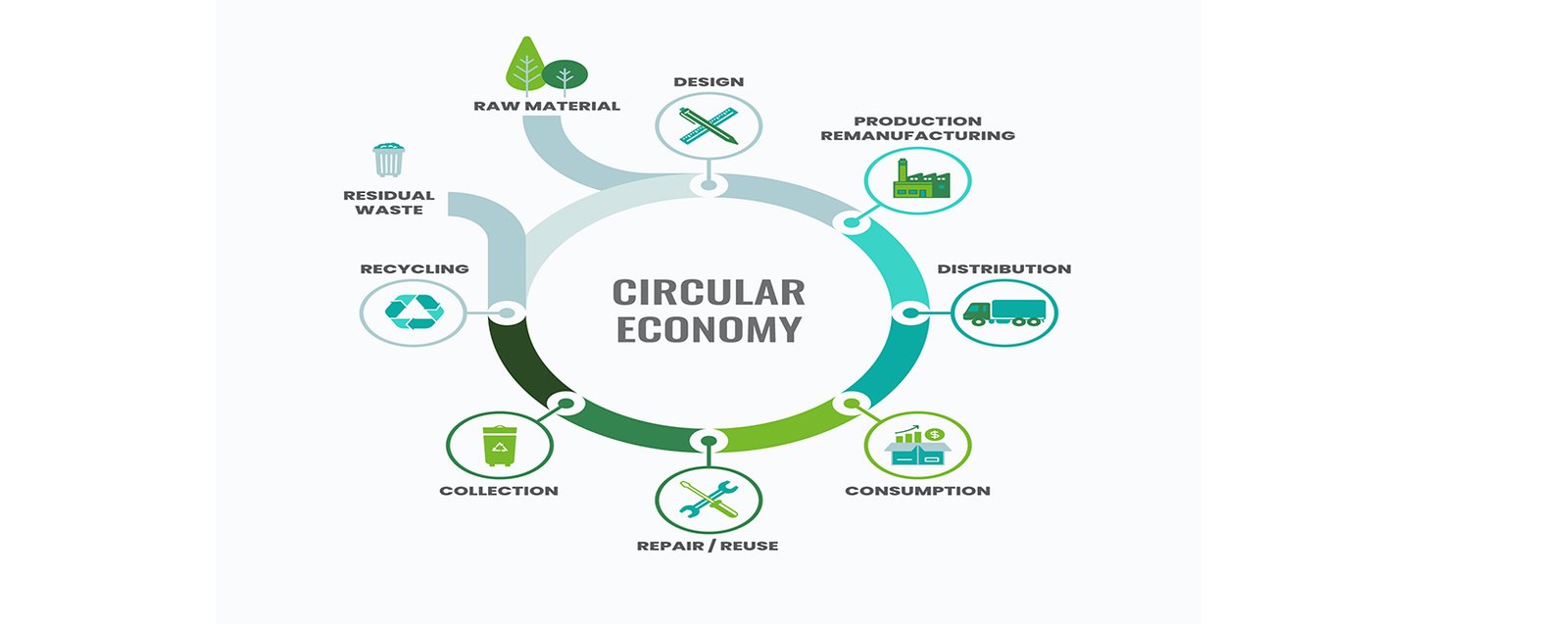
One of the most promising aspects of Zero Waste Discharge Technology is its contribution to the development of a circular economy. In a circular economy, products are designed to last longer, be repaired, and, when they reach the end of their life cycle, are recycled to recover valuable materials. This model is in stark contrast to the traditional linear economy, where products are made, used, and discarded.
By embracing ZWDT, we can:
- Extend the lifecycle of electronic devices through repair and refurbishment.
- Recover and reuse valuable materials in the production of new electronics, reducing the demand for raw materials.
- Minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal processes.
The shift toward a circular economy not only helps to reduce waste but also promotes economic growth, as new industries emerge around recycling, repair, and resource recovery.
Conclusion
The e-waste crisis presents a monumental challenge, but it also offers an opportunity for innovation and sustainability. Zero Waste Discharge Technology is leading the way in responsible recycling practices by ensuring that no harmful materials are released into the environment during the recycling process.
At Advaya E-Waste Management, we are committed to utilizing zero waste discharge technology to protect the environment and promote a circular economy. By choosing responsible e-waste management practices, businesses and individuals can make a positive impact on the planet, reduce pollution, and conserve valuable resources.
Together, we can pave the way for a future where sustainable e-waste management is the standard, and zero waste discharge becomes the norm.





Zero Waste Discharge Technology: The Future of Sustainable E-Waste Management